Considerations when specifying and installing an office lift
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
A lift is arguably the spine of any building. As well as providing structural support, it offers access and transportation to occupants. Careful planning is essential when installing a new lift, needing to be functional and safe.
[edit] Capacity
Before any type of planning can begin, you will need to know the expected capacity of your building along with expected passenger waiting times, as these factors will impact your overall lift requirements. There are guidelines to refer to in order to calculate this, which take into consideration the building’s function, the number of occupants and how they are distributed throughout the building. For example, when there are more than 20 floors, a single grouping would not be ideal as it would result in long travel times and could easily become congested during busy times during the day.
[edit] Environment
The environment that your lift is going to be installed will need to be assessed to help your installer decide on the best way not only to fit your lift, but which design will suit your requirements best. Aspects ranging from how many floors the lift must service to how much weight it has to bear must be considered when evaluating the proposed space.
[edit] Peak times
Peak times and high traffic locations must be considered. A restaurant on the first floor may cause serious congestion during the lunchtime rush, and your lift will not travel much further than the first floor because it will be transporting hungry passengers. Similarly, you could experience problems in the morning as people arrive, and maybe stop to get their breakfast and morning coffee. To avoid these issues, consider locating the central food hub on the ground floor, or if you can, create a dining areas at the top of your building; you could then consider having a separate lift systems to take passengers directly to the restaurant.
[edit] Safety
This is perhaps one of the most important issues to consider. The lift should be able to bear the weight of people when at maximum capacity, and needs to be fitted with a functioning alarm system that can be used if the lift were to break down.
In the UK, lifts installed to be used by people in the workplace are subject to the Lifting Operations and Lifting Equipment Regulations (LOLER) and Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations 1998 (PUWER).
The business (duty holder) is legally responsible for ensuring that the lift is examined and is safe to use. In addition to routine maintenance, detailed and thorough examinations of the lift need to be carried out regularly by a competent person.
[edit] Lift design
While safety is paramount when planning to instal a lift, a good installation should also focus on the aesthetics of the lift. If your lift is being installed in a new, modern office or another more refined environment, it is important that it ties in with the overall design and décor of the building. However, bear in mind that as much as scenic, glass lifts look attractive, the more complicated the lift design, the more complicated it will be to maintain. Scenic lifts generally work best in low rise buildings or in collaboration with standard passenger lifts and escalators.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Access and inclusion in the built environment: policy and guidance.
- Access consultant.
- Approved document M.
- Changing lifestyles.
- Fire and rescue service.
- Firefighting lift.
- Hoists.
- Inclusive design.
- Lifts.
- Lifts for office buildings.
- Lifting Operations and Lifting Equipment Regulations (LOLER).
- Non-discriminatory building design.
- Railings.
- Ramps.
- Shanghai Tower.
- Stairs.
Featured articles and news
Sustainable Urban Drainage and Biodiversity
Awards for champions of these interconnected fields now open.
Microcosm of biodiversity in balconies and containers
How minor design adaptations for considerable biodiversity benefit.
CIOB student competitive construction challenge Ireland
Inspiring a new wave of Irish construction professionals.
Challenges of the net zero transition in Scotland
Skills shortage and ageing workforce hampering Scottish transition to net zero.
Private rental sector, living standards and fuel poverty
Report from the NRH in partnership with Impact on Urban Health.
.Cold chain condensing units market update
Tracking the evolution of commercial refrigeration unit markets.
Attending a conservation training course, personal account
The benefits of further learning for professsionals.
Restoring Alexander Pope's grotto
The only surviving part of his villa in Twickenham.
International Women's Day 8 March, 2025
Accelerating Action for For ALL Women and Girls: Rights. Equality. Empowerment.
Lack of construction careers advice threatens housing targets
CIOB warning on Government plans to accelerate housebuilding and development.
Shelter from the storm in Ukraine
Ukraine’s architects paving the path to recovery.
BSRIA market intelligence division key appointment
Lisa Wiltshire to lead rapidly growing Market Intelligence division.
A blueprint for construction’s sustainability efforts
Practical steps to achieve the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
Timber in Construction Roadmap
Ambitious plans from the Government to increase the use of timber in construction.
ECA digital series unveils road to net-zero.
Retrofit and Decarbonisation framework N9 launched
Aligned with LHCPG social value strategy and the Gold Standard.
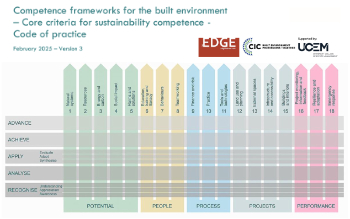
Competence framework for sustainability
In the built environment launched by CIC and the Edge.
Institute of Roofing members welcomed into CIOB
IoR members transition to CIOB membership based on individual expertise and qualifications.
Join the Building Safety Linkedin group to stay up-to-date and join the debate.
Government responds to the final Grenfell Inquiry report
A with a brief summary with reactions to their response.